Diesel engine and Diesel Engine Timing Setting

Head Wall: The engine valve that helps the engine take in air and release carbon dioxide. When the piston takes in oxygen the piston starts moving downwards. 
As soon as it starts coming up, both the head engine valve close. The piston is at the top, only then the diesel oil burns. Then due to pressure on the piston, the piston moves downwards and when it comes up for the second time, the head engine valve starts opening and the burnt smoke comes out! When the piston goes down for the third time the oxygen valve opens and when the piston comes up for the fourth time both valves close. This process keeps happening again and again and the engine keeps rotating.
Working of Engine Pump and Cam Soft Pinion: All these pinions are connected to the engine crank but the cam soft and pump pinion teeth are always twice the teeth of the crank pinion. When the crank rotates twice, the pump pinion and wall cam pinion rotate once, thereby timing the action of oil, air and carbon-dioxide.
Diesel engine and Diesel Engine Timing Setting 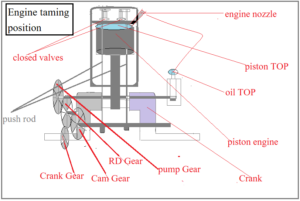
This means that the engine pump and cam soft have to operate at the correct time. Because to rotate the engine, the piston crank, diesel pump and cam soft have to be set at the same time.
Many engine mechanics are always curious to know the engine taming setting. The vle.one owner has made many engine taming settings, which is why vle.one is proud to say today! The taming of almost all four stock engines is the same, the only difference is that in a diesel engine, when the piston comes up, the diesel will be expelled through the nozzle. In a petrol engine, when the piston reaches the top, electricity is generated which burns the oil. Due to burning of oil, excessive pressure on the piston causes the piston to rotate the crank.
How to make the first taming setting of a diesel engine: Engine taming setting is very simple. When the piston is at the top, the valve is completely closed. At such a time, the piston of the diesel pump also gets ready to supply oil to the nozzle. As the piston starts to move down 1 mm, oil is poured onto the piston through the nozzle. And the firing timing setting of diesel engine is done as per EC regulations.
How to Set Diesel Engine 2ST Wall Taming: Diesel Engine Wall Taming is an important setting of diesel engine. If the timing of the engine valve goes wrong then in such a situation a collision occurs between the engine valve and the piston due to which the engine valve and the piston get damaged and the engine valve bends. It is important to note that when the piston comes to the top twice, the engine valve cam pinion rotates slowly and the oil pump pinion rotates only once. Since the piston comes to the top first, the setting to control the engine valve is done first. First the piston is raised completely, after this the Wall Cam Soft is installed in such a way that when the Wall Cam Soft is rotated 1 mm to the right and 1 mm to the left, the engine valve gets pressed. Now connect it to the piston’s crank at this location using a pinion or toothed belt. Now when the piston comes up for the second time, all the engine valve should be closed. At this time the tappet should move 1 mm and at this time the oil is expelled through the nozzle. After setting the wall taming, the engine has to be rotated once and checked. If all settings are correct the engine will rotate smoothly. Now before starting the engine, the engine should be started only after checking the Mobil oil, water and everything else.
Diesel Engine Tappet Clearance Setting: Be it a diesel engine or a petrol engine, all four stock engines require tappet clearance to function properly. The tappet is connected at the time when the piston is at the top, both valves are closed and the nozzle is fired with diesel pump oil when the piston is at the top. Only then about 0.3 MM clearance is left for the tappet or the clearance is left as per the company’s engine.







